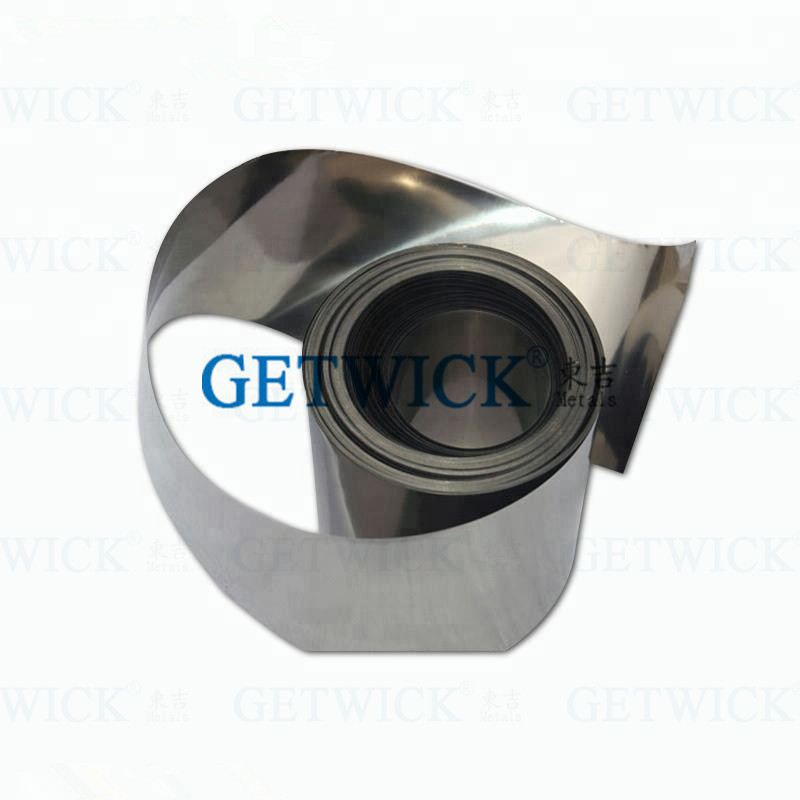
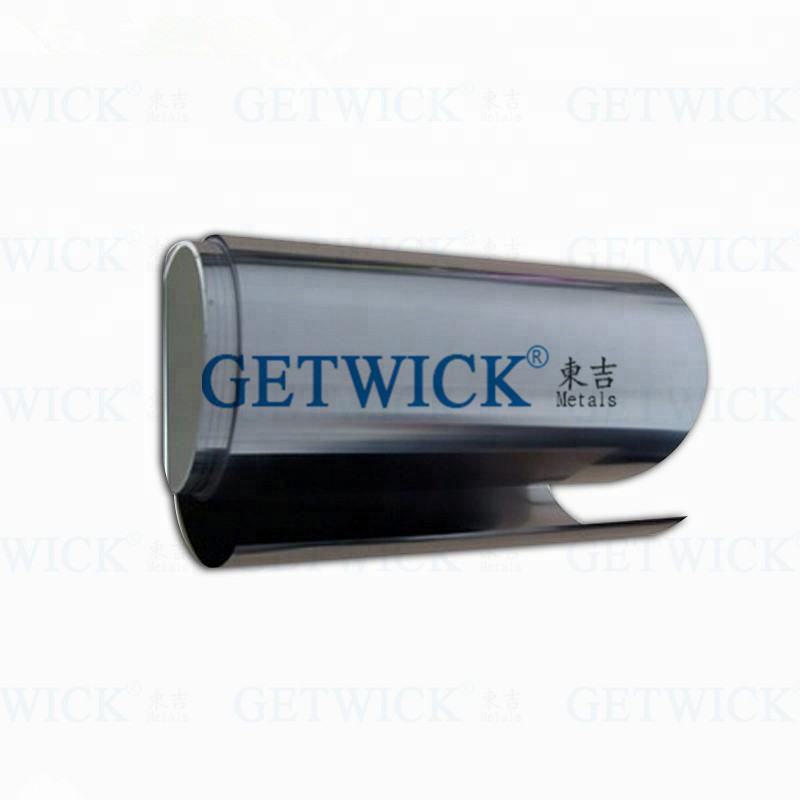
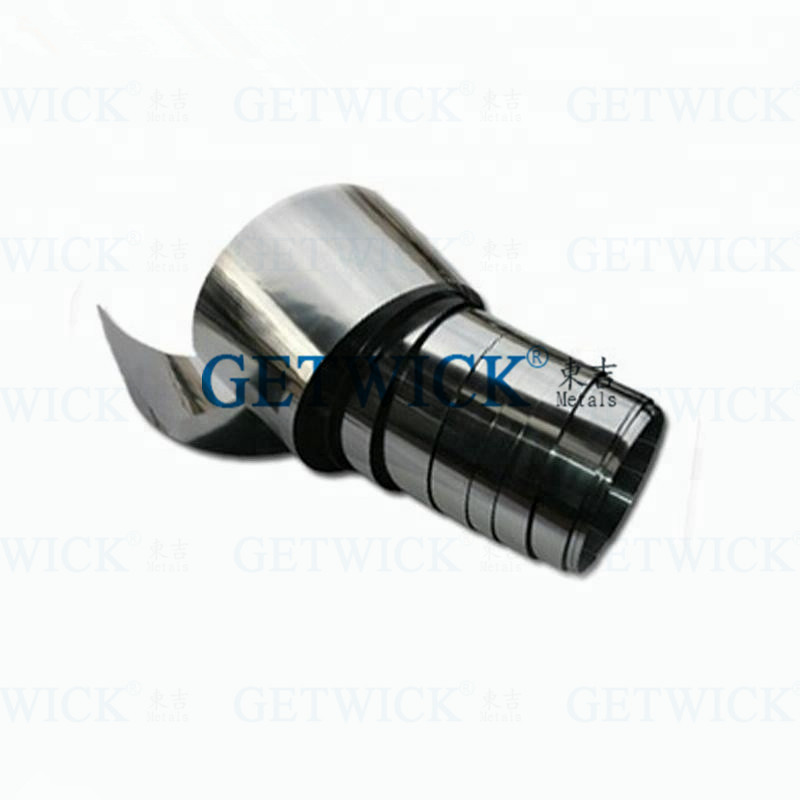
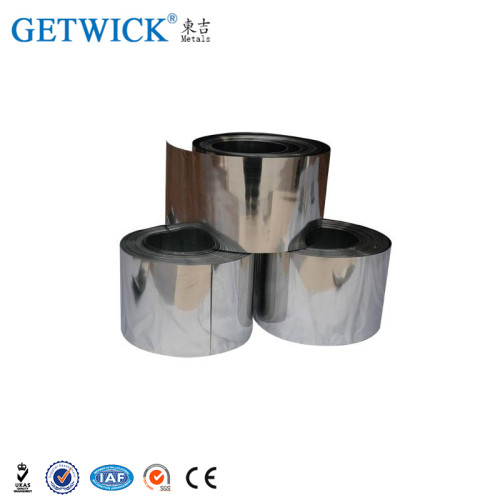
TZM Molybdenum Alloy Ribbon Foil From GETWICK
- Model
- MLa, 364
Item specifics
- Key product
- 2018 Hot Sale TZM Molybdenum Alloy Ribbon Price
- Standard
- ASTM B386
- Material
- Ti, Zr, Mo alloy
- Grade
- TZM, 364
- Melting temperature
- 2610 Centigrade
- Working temperature
- 1300-1400 Centigrade
- Dimension
- T0.025mm min. x W300mm max. x Coil
- Surface
- Cold rolling bright
- Certificate
- ISO9001:2015, SGS, BV
- Application
- High temperature furnace industry
Review
Description
TZM Molybdenum Alloy Ribbon Foil From GETWICK
With its unique mechanical and chemical properties, molybdenum is an outstanding material that can meet the most exacting requirements. Because molybdenum possesses a very high melting point, a low coefficient of thermal expansion and a high level of thermal conductivity, it is used in many different industries. Molybdenum is a genuine all-rounder. We use this material, for example, to produce ribbons and wires for the lighting industry, semiconductor base plates for power electronics, glass melting electrodes, hot zones for high-temperature furnaces and sputtering targets for coating solar cells and flat screens.
| Standard | ASTM B386 |
| Grade | Mo1 |
| Density | 10.2g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2610 Centigrade |
| Using Temperature | 1300-1400 Centigrade |
| Purity | 99.95% min. |
| Size | User's demand |
| Colour | Bright |
| Package | Standard wooden case or as your request |
Feature
1. Low thermal expansivity
2. High using temperature
3. Good corrosion resistence
4. High strength
5. Low electrical resistivity
6. Manufacturing based on customer’s request
Application
1. Special evacuated tube
2. Heating element
3. Can also be used in high temperature furnace and glass industries, etc.
Chemical requirements
Concentration(%) 0.003 0.002 0.005 0.0001 0.002 0.0001 0.002 0.0001 0.002 0.001 0.01 0.003 0.003 0.0005
Element Ni Mg Fe Pb Al Bi Si Cd Ca P C O N Sb
Concentration(%) 0.003 0.002 0.005 0.0001 0.002 0.0001 0.002 0.0001 0.002 0.001 0.01 0.003 0.003 0.0005